
Patients are given special liver medicines to control the infection. The complications of liver cirrhosis include liver cancer, swelling of the legs, increased risk of bleeding, water retention and jaundice.Īt Nobel Gastroenterology Centre, we manage individuals with chronic Hepatitis B and evidence of liver damage either on blood tests or an ultrasound scan.

Over several years, this may result in permanent liver damage called liver cirrhosis. Other individuals with Hepatitis B may experience low-grade liver inflammation. A severe flare can result in liver failure and even death, if it is not treated early. Some Hepatitis B carriers may develop an acute Hepatitis B flare that is characterised by jaundice, lethargy, nausea and right-sided abdominal pain. This implies that the individual has the virus circulating in the blood without any symptoms or liver damage. The most common form of Hepatitis B infection is a carrier state (Hepatitis B carrier). Individuals at risk of liver failure are those with coexisting liver disease and the elderly. When this happens, a liver transplant may be lifesaving. In less than 1% of all infections, liver failure may occur. Medicines are given to support the liver and to treat any symptoms that are present. One’s immune system will combat the virus and eradicate it. A liver test will show severe inflammation of the liver (hepatitis and an elevated bilirubin level). However, after the symptoms abate, one develops lethargy, right-sided abdominal discomfort from liver inflammation, and jaundice. These symptoms are often mistaken for another episode of gastroenteritis (food poisoning). Diarrhoea and fever may be present as well. Hepatitis A presents with nausea and vomiting in the initial stages. What are the symptoms of Hepatitis A & B, and what are the potential complications that it can lead to? Symptoms of Hepatitis A Hence, exposure to medical or dental equipment, and blood products do not increase one’s risk of a Hepatitis B infection. platelet transfusion, red blood cell transfusion) are screened for Hepatitis B virus and the levels of sterility are high.

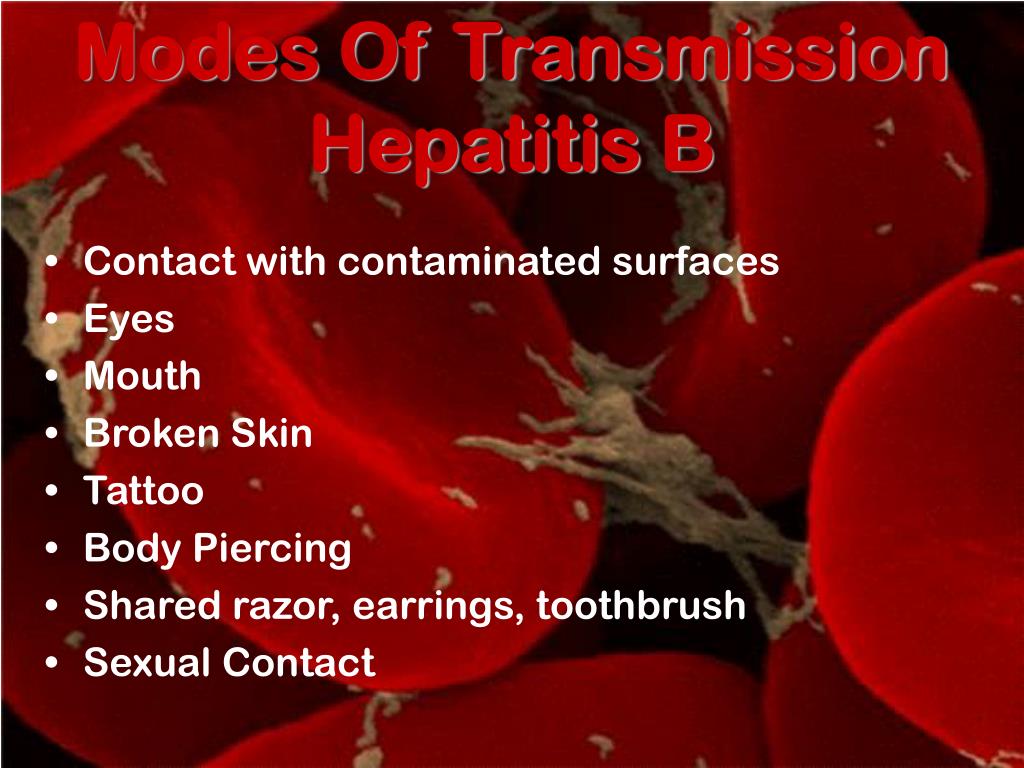
This is called vertical transmission and it results in the child becoming a Hepatitis B carrier. In Asia, the most common mode of Hepatitis B transmission is from a mother to her child during childbirth. The Hepatitis B infection is spread by blood and body fluids. Hence, anyone can get a Hepatitis A infection if the food is contaminated and undercooked or eaten raw. Heat that is generated during cooking inactivates the virus, even if the ingredients are contaminated. A person is at risk of contracting Hepatitis A, if he or she consumes food that is not cooked thoroughly. Hepatitis A is transmitted by ingesting contaminated food and water. Who is at risk of contracting Hepatitis A & B? Hepatitis A
Our liver specialists at Nobel Gastroenterology Centre have treated liver infections caused by other viruses such as Cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus and Herpes simplex viruses. Hepatitis A and B are the most common strains in Singapore.ĭo note that these are not the only viruses that can cause liver disease. These include Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Hepatitis D and Hepatitis E. What are the different strains of Hepatitis? In contrast, Hepatitis B often presents as a liver disease, which is long standing and chronic in nature. Hepatitis A causes an illness, which is short-lived and self-limiting. They are often confused with each other, but in fact, they are actually very different. Hepatitis A and B are viruses, which can infect the human liver and cause liver disease. Paediatric Intervention (HeadStart for Life).Speech Therapy (Amazing Speech Therapy).Paediatric Surgery (Nobel Paediatric Surgery Centre).Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition.General Surgery & Colorectal Surgery (TEN Surgery).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
